Endocannabinoid System 101
Do I have an endocannabinoid system? The answer is yes, yes you do.
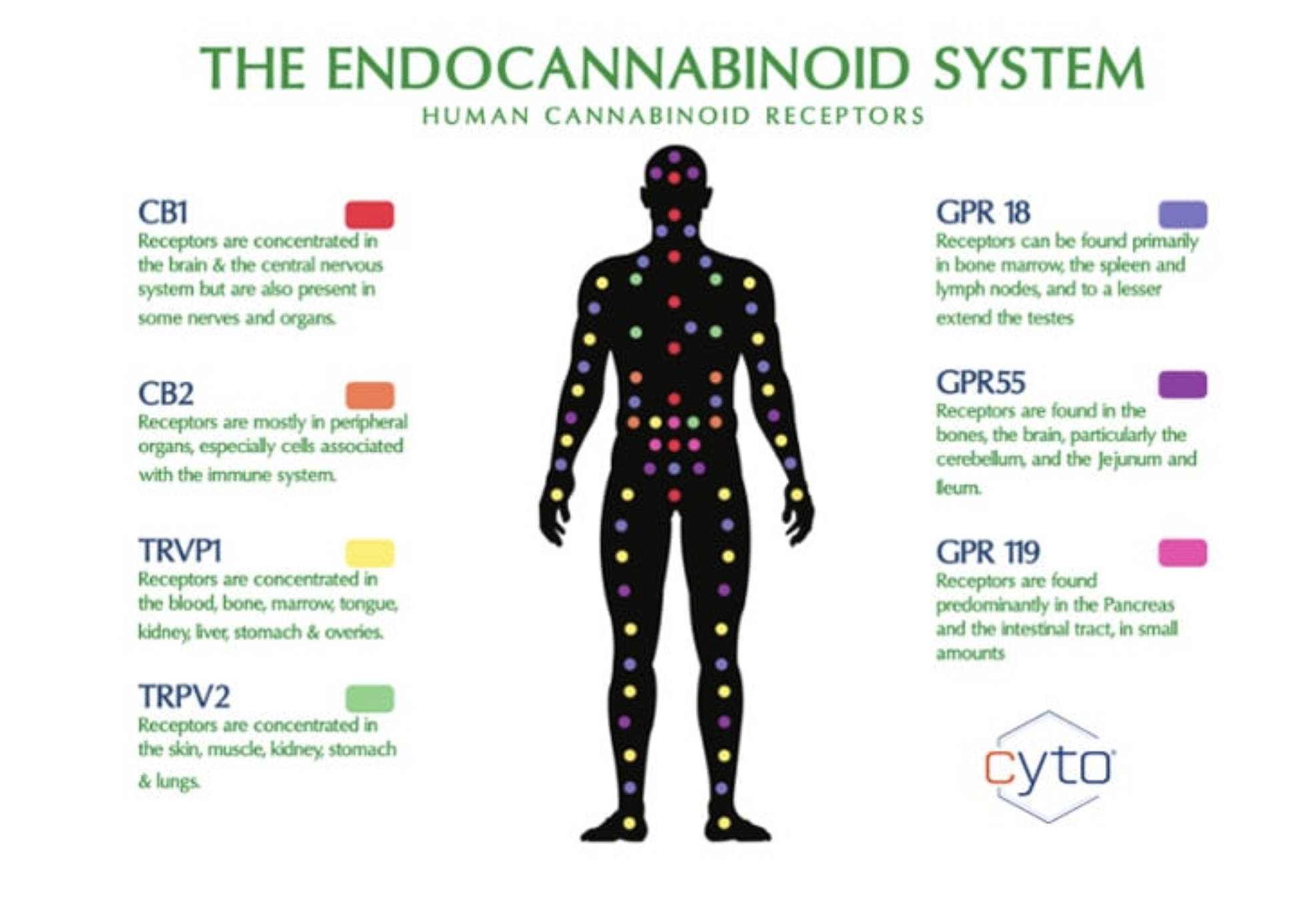
The endocannabinoid system is an active and complex cell signaling network. It involves a combination of endocannabinoids, enzymes, and cannabinoid receptors that help regulate several functions in the human body.
The discovery of the ECS is relatively new. In the early 1990sTrusted Source, a chemist isolated the first endocannabinoid in the human brain. Since that time, researchers have been learning more about this system and the role it plays in bodily functions.
Endocannabinoids are similar to the cannabinoids present in the cannabis sativa (C. sativa) plant. However, the human body naturally produces endocannabinoids. The term “endo” refers to “within,” as in within the body.
The human body naturally produces endocannabinoids. They are present in various organs and tissues, such as the muscle, brain, and circulating cells. Endocannabinoids become active when they bind with a cannabinoid receptor. The receptors are also located throughout the body.
Research continues on the exact physiological mechanism that promotes or triggers the binding of the receptors to the endocannabinoids. But experts theorize that when a system in the body is out of balance, the receptors bind to the cannabinoids to help correct the problem.
The endocannabinoid system is precise. For example, if body temperature is out of the normal range, the ECS regulates it without altering other processes. Once the ECS brings the body back into balance, the enzymes break down the cannabinoids to prevent overcorrecting the problem.
The function of cannabinoids within the ECS is vast. In fact, researchers still do not fully understand the exact role of cannabinoids, although the ECS clearly plays a large part in how well the body functions.
Research suggests that the ECS plays a key role in contributing towards homeostasis. Homeostasis refers to the maintenance of stability, or optimal conditions, within the body to promote proper functioning.
For example, the body maintains homeostasis for temperature, blood sugar, and appetite. Experts believe that if the body falls out of the normal range, the ECS helps the body to return to the optimal range and maintain homeostasis.
Research indicates that the ECS may containTrusted Source multiple promising therapeutic targets. While the body can produce endocannabinoids, there are also many cannabinoids present in the C.sativa plant which are of medical interest.
Two of the most well-known cannabinoids include tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD). They can also bind to cannabinoid receptors and produce similar effects to endocannabinoids. THC is the cannabinoid that causes the “high” that people may associate with cannabis, whereas CBD does not produce this sensation.
Studies are ongoing to determine the therapeutic benefits of cannabinoids. For example, a 2016 studyTrusted Source investigated the effect of CBD on joint inflammation in rats. The study suggests that applying a topical gel containing CBD decreased pain and joint swelling in rats without side effects.
*Credit for this content goes to this Medical News Today article which can be seen in its unabridged form by clicking HERE.
